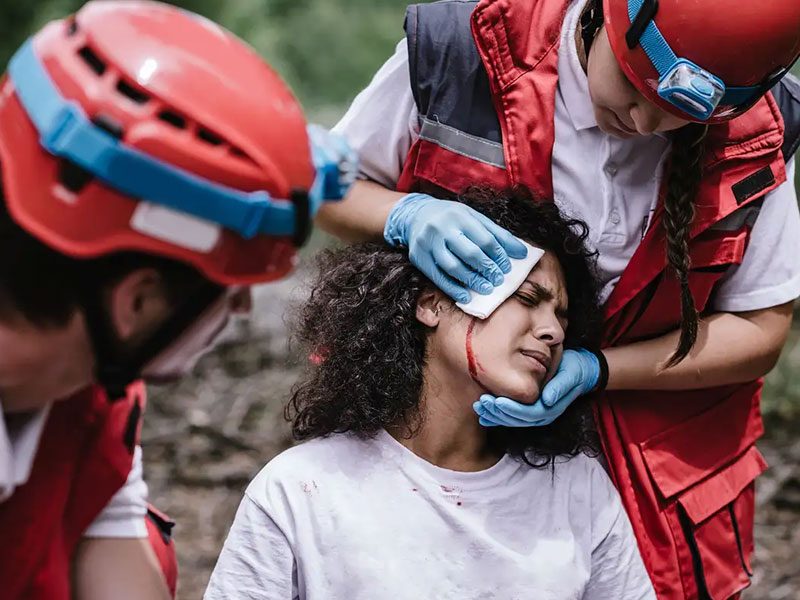

A head injury is any trauma to the scalp, skull, or brain. The injury may be only a minor bump on the skull or a serious brain injury. Head injury can be either closed or open (penetrating). A closed head injury means you received a hard blow to the head from striking an object, but the object did not break the skull. An open, or penetrating, head injury means you were hit with an object that broke the skull and entered the brain. This is more likely to happen when you move at high speed, such as going through the windshield during a car accident. It can also happen from a gunshot to the head.
Head injuries include:
Head injuries may cause bleeding:
In the brain tissue
In the layers that surround the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, extradural hematoma) Head injury is a common reason for an emergency room visit. A large number of people who suffer head injuries are children. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) accounts for over 1 in 6 injury-related hospital admissions each year.
Causes
Symptoms
First Aid
Learning to recognize a serious head injury and give basic first aid can save someone's life. For a moderate to severe head injury, CALL 911 RIGHT AWAY.
Then take the following steps:
1. Check the person's airway, breathing, and circulation. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
2. If the person's breathing and heart rate are normal, but the person is unconscious, treat as if there is a spinal injury. Stabilize the head and neck by placing your hands on both sides of the person's head. Keep the head in line with the spine and prevent movement. Wait for medical help.
3. Stop any bleeding by firmly pressing a clean cloth on the wound. If the injury is serious, be careful not to move the person's head. If blood soaks through the cloth, do not remove it. Place another cloth over the first one.
4. If you suspect a skull fracture, do not apply direct pressure to the bleeding site, and do not remove any debris from the wound. Cover the wound with sterile gauze dressing.
5. If the person is vomiting, to prevent choking, roll the person's head, neck, and body as one unit onto their side. This still protects the spine, which you must always assume is injured in the case of a head injury. Children often vomit once after a head injury. This may not be a problem, but call a doctor for further guidance.
6. Apply ice packs to swollen areas (cover ice in a towel so it does not directly touch the skin).
Follow these precautions:
DO NOT wash a head wound that is deep or bleeding a lot.
DO NOT remove any object sticking out of a wound.
DO NOT move the person unless absolutely necessary.
DO NOT shake the person if they seem dazed.
DO NOT remove a helmet if you suspect a serious head injury.
DO NOT drink alcohol within 48 hours of a serious head injury.
A serious head injury that involves bleeding or brain damage must be treated in a hospital.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Prevention
